Bronchioles Definition
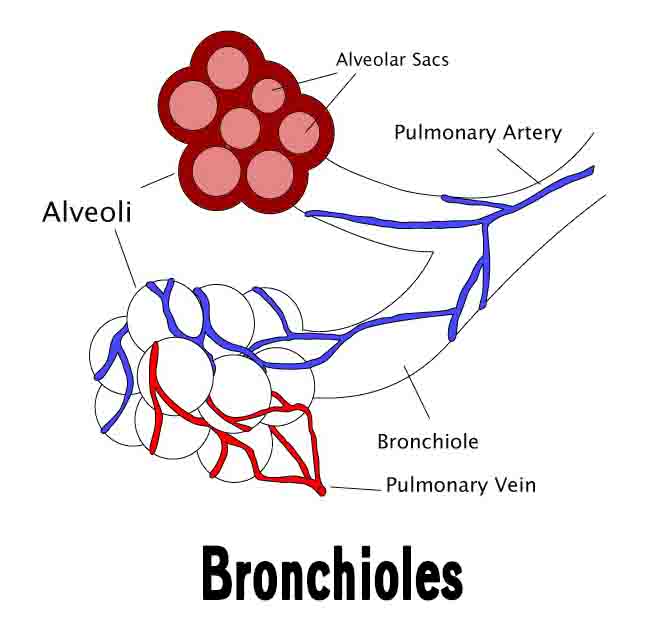
In the lungs, bronchioles branch off from the larger bronchi which enter each lung, from the large and singular trachea that connects the mouth with the lungs. The bronchioles are one of the smallest airways in the respiratory tract, and they lead directly to the alveolar ducts which contain the alveoli responsible for exchanging gases with the blood.
Near the number 2 in the image above, each bronchus divides into secondary and tertiary bronchi, which get smaller and smaller. As the bronchi lose some of their structural elements, they become bronchioles.
There is no hyaline cartilage surrounding the bronchioles, which prevents the bronchi from collapsing. It is instead the tissues to which they carry air that anchor the bronchioles. The smooth muscle tissue that surrounds each bronchiole also supports the bronchioles.
The smooth muscle tissue in the bronchioles can sometimes contract, reducing their size. Patients with asthma and other lung diseases often experience bronchospasms.
A bronchiole is one of the pulmonary lobules of the lungs. As the bronchioles divide, they form smaller terminal bronchioles, which divide into the smallest respiratory bronchioles. In the respiratory bronchioles, alveoli surround the bronchioles and the walls become thin enough to allow gas exchange.
Function of the Bronchioles
Between the large cartilage-supported bronchi that enter the lungs and the tiny alveolar ducts that connect directly to the alveoli are the bronchioles. Air rich in oxygen is carried into the lungs by the bronchioles, and carbon dioxide is carried out of the lungs by the bronchioles, so that breathing and respiration can occur.
A smooth muscle surrounding the bronchioles can constrict or dilate the airway, helping the blood receive the right amount of oxygen.
Related Biology Terms
- Pulmonary Lobule – A functional unit of lung tissue containing tissue blood vessels and airways, which are fed by bronchioles.
- Bronchi – The large airways that branch off of the main trachea, and supply each lung with air.
- Hyaline Cartilage – Rings of a hard material, seen in several joints and in rings that surround the trachea and bronchi.
- Respiratory Tract – The entire system of airways which connect the mouth to the alveoli responsible for exchanging gases with the blood vessels in the lungs.