Sarcolemma Definition
There are striated muscle fiber cells surrounded by a specialized membrane called the sarcolemma. Like the plasma membrane, the sarcolemma has specialized functions for muscle cells and is sometimes referred to as the myolemma.
In addition to the extracellular matrix, the sarcolemma contains polysaccharides that allow the cell to anchor into the tissue that builds and supports muscle fibers. It creates a very strong fiber that can contract with other muscles by connecting the basement membrane, which surrounds all connective tissues.
Function of the Sarcolemma
As well as providing structure and resources for muscle cells to function, the sarcolemma has several unique characteristics. In comparison with some cell membranes, the sarcolemma must be continuously maintained in order to cover the many myofibrils that make up a muscle cell.
Sarcolemma of one cell attaches to sarcolemma of the opposite cell, eventually forming tendons that connect muscles to bones. Muscle cells generate movement in the body by contracting against these levers.
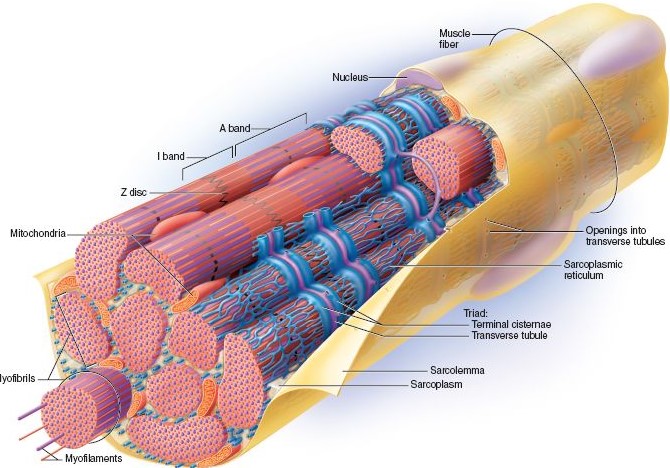
Because these contractions require a large amount of energy, the sarcolemma is specially formed with channels that allow materials to flow into and out of the cell. According to the picture below, these small entry points form channels throughout muscle cells that carry glucose, nutrients, and ions to mitochondria.
A motor neuron’s signal to contract a muscle disrupts the membrane potential of these channels. An action potential is generated by the sarcolemma in response to the signal sent by the neuron, causing the proteins within the cell to contract.
Apart from its specialized functions, the sarcolemma functions as a normal cellular membrane. A number of embedded proteins control the contents of the cell in concert. Sarcolemma membranes are composed of phospholipids, which influence the flow of water, ions, and other molecules.
Different species of sarcolemma may have different proteins and compositions, reflecting their evolutionary needs over time.
Related Biology Terms
- Cell Membrane – A double layer of phospholipids which surrounds.
- Basement Membrane – The lowest layer of the epithelium, made from a number of proteins and polysaccharides.
- Action Potential – An electrical impulse created by the rapid diffusion of ions across a cell membrane.
- Motor Neuron – Specialized nerves which carry signals exclusively to muscle cells.